Why Are There So Many Different Types of “X”aaS?
Chances are good that you’ve heard of (or at least seen) the term SaaS at some point. SaaS stands for Software as a Service, which is the technical term for cloud computing. Of course, software is not the only thing that can be provided as a service from the cloud, and this explains why there are so many different terms ending in -aaS.
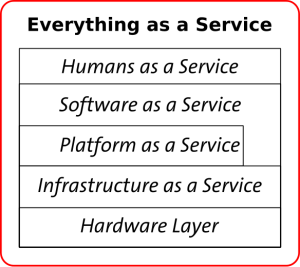
Understanding the Cloud Computing Stack
There are three distinct categories that makeup cloud computing in its entirety. If you think of cloud computing as a pyramid divided into three horizontal sections, SaaS would make up only the very top section of that pyramid. Below it, you’ll find PaaS, which stands for Platform as a Service, making up the middle section. Finally, at the base is IaaS, which stands for Infrastructure as a Service. Understanding how each of these work independently is the key to understanding how they all work together, as well.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Simply put, SaaS refers to any software that is deployed via the internet. A provider licenses an application or software to customers on demand, via a subscription, or even through pay-as-you-go models. SaaS is incredibly popular in a variety of small and large businesses alike where many individuals need access to an application, and this is particularly true in situations where purchasing licenses for each user would be incredibly costly. The provider also handles all upgrades, maintenance, and repair, which takes much of the stress off of the businesses.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service, or PaaS, has all of the same benefits of SaaS, but with one major difference: it is designed with software development in mind rather than the actual deployment of software. Essentially, a provider gives the end users of PaaS a platform for software creation that is delivered via the web rather than purchased and downloaded locally. It is perfect when multiple developers need to work on a project together or when a company needs to bring in third parties from other companies to help with the processes.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Finally, at the base of the pyramid is Infrastructure as a Service or IaaS. This can be described as a method of delivering cloud computing infrastructure, consisting of servers, storage, operating systems, and even networks, to businesses as an on-demand service. This way, companies are not required to purchase their own data center equipment as there is no need to have a data center on-site. Companies can purchase everything they need as an outsourced service, and the best part is that they can pay for only what they need as they need it. This makes the infrastructure itself incredibly scalable; this is not true for on-site infrastructure that is difficult to scale to suit the demands of a growing business.
Although many businesses make use of SaaS, there are a growing number of companies that are also subscribing to PaaS and IaaS thanks to their ability to save time and money. In fact, in today’s day and age, many businesses are beginning to understand the benefits of subscribing to all three.
The post Why Are There So Many Different Types of “X”aaS? appeared first on SDTEK | San Diego, CA.